
Seeing Is Believing: The Benefits of Ultrasound for Patients and Providers
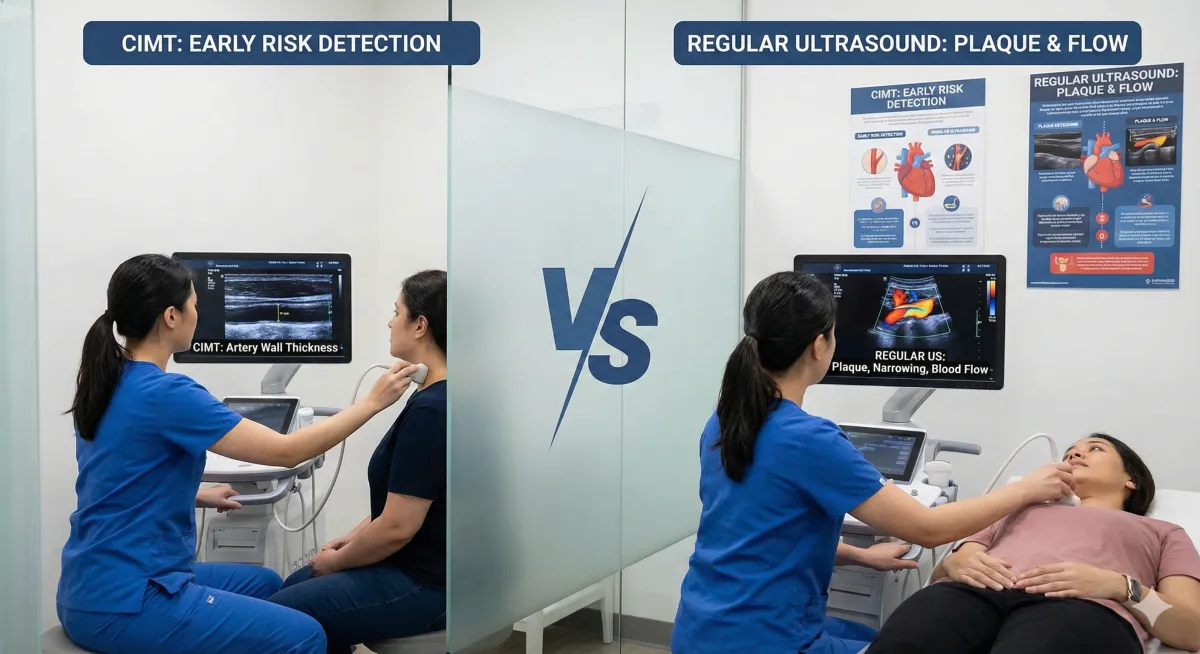
CIMT vs Regular Carotid Ultrasound: What’s the Difference?
CIMT vs Regular Carotid Ultrasound: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to assessing cardiovascular health, ultrasound technology plays a crucial role. Two common types of carotid ultrasounds are used to evaluate the health of the carotid arteries: the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test and the regular carotid ultrasound. Although both are non-invasive and highly effective in detecting artery issues, they serve different purposes and provide different kinds of information about heart health. Let’s break down the key differences between these two tests to help you understand when each one is used and how they can benefit you.

What is a Regular Carotid Ultrasound?
A regular carotid ultrasound is a routine imaging procedure used to evaluate the carotid arteries, which are located in the neck and supply blood to the brain. This test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the arteries and detect any blockages or narrowing (stenosis) caused by plaque buildup, which is often due to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). The goal of a regular carotid ultrasound is to measure the degree of blockage or narrowing of the arteries, which can help determine the risk of stroke or other cardiovascular events.
What a Regular Carotid Ultrasound Detects:
Blockages or narrowing of the carotid arteries
Plaque buildup (atherosclerosis)
Blood flow patterns and velocity
When is it Recommended?
When you have a family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease
If you’re experiencing symptoms such as dizziness, vision problems, or fainting
To monitor existing conditions like high cholesterol or hypertension
What is a CIMT (Carotid Intima-Media Thickness) Test?
The CIMT test, on the other hand, is a specialized ultrasound that focuses on measuring the thickness of the walls of the carotid arteries, specifically the intima and media layers. The thickness of these arterial layers is a key indicator of how much plaque is building up over time. A CIMT test provides more detailed information about the early stages of artery thickening and can detect subclinical (early-stage) atherosclerosis before any visible blockages or symptoms develop.

What a CIMT Test Detects:
Thickening of the arterial walls, which is an early sign of atherosclerosis
The potential for future cardiovascular risk, even in the absence of visible plaque buildup
The progression of plaque accumulation over time
When is it Recommended?
To assess early signs of cardiovascular disease in individuals without symptoms
If you have risk factors such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or smoking but no clear signs of artery narrowing
To monitor the progression of atherosclerosis over time
Key Differences Between CIMT and Regular Carotid Ultrasound
Purpose:
Regular Carotid Ultrasound: Focuses on detecting existing blockages or narrowing in the arteries.
CIMT Test: Focuses on detecting early signs of atherosclerosis by measuring arterial wall thickness.
What They Measure:
Regular Carotid Ultrasound: Measures the flow of blood and identifies blockages caused by plaque buildup.
CIMT Test: Measures the thickness of the artery walls, which can predict future cardiovascular risks.
What They Detect:
Regular Carotid Ultrasound: Detects current plaque buildup or blockages in the arteries that can lead to strokes.
CIMT Test: Detects the early stages of atherosclerosis before blockages occur, providing a preventive measure for long-term health.
Risk Assessment:
Regular Carotid Ultrasound: Offers a snapshot of current arterial health, particularly in relation to stroke risk.
CIMT Test: Offers insight into the potential for future heart disease, allowing for earlier intervention.
Why is CIMT a Valuable Test?
While a regular carotid ultrasound is critical for detecting advanced issues like blockages, the CIMT test allows doctors to intervene before those issues become severe. By detecting thickened arterial walls, healthcare providers can recommend preventive treatments such as lifestyle changes, medications, or more frequent monitoring. The CIMT test is especially valuable for individuals with risk factors but no apparent symptoms, as it can help identify hidden cardiovascular risks early on.
Which Test is Right for You?
The decision between a CIMT test and a regular carotid ultrasound often depends on your personal health history, risk factors, and symptoms. If you have a family history of cardiovascular disease or are experiencing symptoms like dizziness or fainting, a regular carotid ultrasound may be the first step. However, if you're looking for a more proactive approach to understanding your heart health, especially if you have risk factors like high cholesterol or high blood pressure, a CIMT test could provide the insights you need.
Conclusion
Both the regular carotid ultrasound and CIMT test are valuable tools in the early detection and prevention of cardiovascular disease, each serving a unique purpose. Regular carotid ultrasounds are essential for identifying blockages and assessing stroke risk, while CIMT tests offer a preventive measure by detecting early signs of artery thickening before blockages occur. If you're unsure which test is right for you, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your individual risk factors and determine the most appropriate screening.
Understanding the differences between these two ultrasound tests is the first step toward taking control of your cardiovascular health, allowing for timely interventions and a healthier future.
For those seeking expert ultrasound services, Atlanta Ultrasound offers quick, efficient, and comprehensive scans. Our team of skilled professionals is dedicated to providing you with the clarity and care you need.
Contact us today to schedule your ultrasound scan and take a decisive step towards understanding your health.
📍 Multiple locations in Metro Atlanta, GA
📞 Contact: 678-590-3300
🌐 Website:www.atlantaultrasound.com
Disclaimer: The content of this blog post, authored by a sonographer, is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical advice, nor should it substitute for professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or health concerns.
